Learn about embedded systems security, including the required design methodology and implementation needed for securing today’s embedded systems.
Embedded systems security is a design methodology, implementation, and commitment that companies embrace to limit the threat exposure of the devices they build and the data these devices generate. Security for embedded devices is a full lifecycle responsibility. It starts well before the first line of code is written, includes protection in case a device falls into the hands of attackers, and continues until a device has been decommissioned.
IDC estimates that by 2025, there will be more than 55 billion connected devices.
Every company should have a security policy in place before an embedded project is approved and started. A security policy is a written and agreed-upon strategy and plan to address the full lifecycle security needs of the product and its data, including design, testing, delivery, maintenance, and decommissioning at end-of-life. Project teams need to fully understand the risks associated with a security breach that impacts their product. In addition, security requirements need to be agreed upon for the individual devices, the communications between devices, the network, and the data.
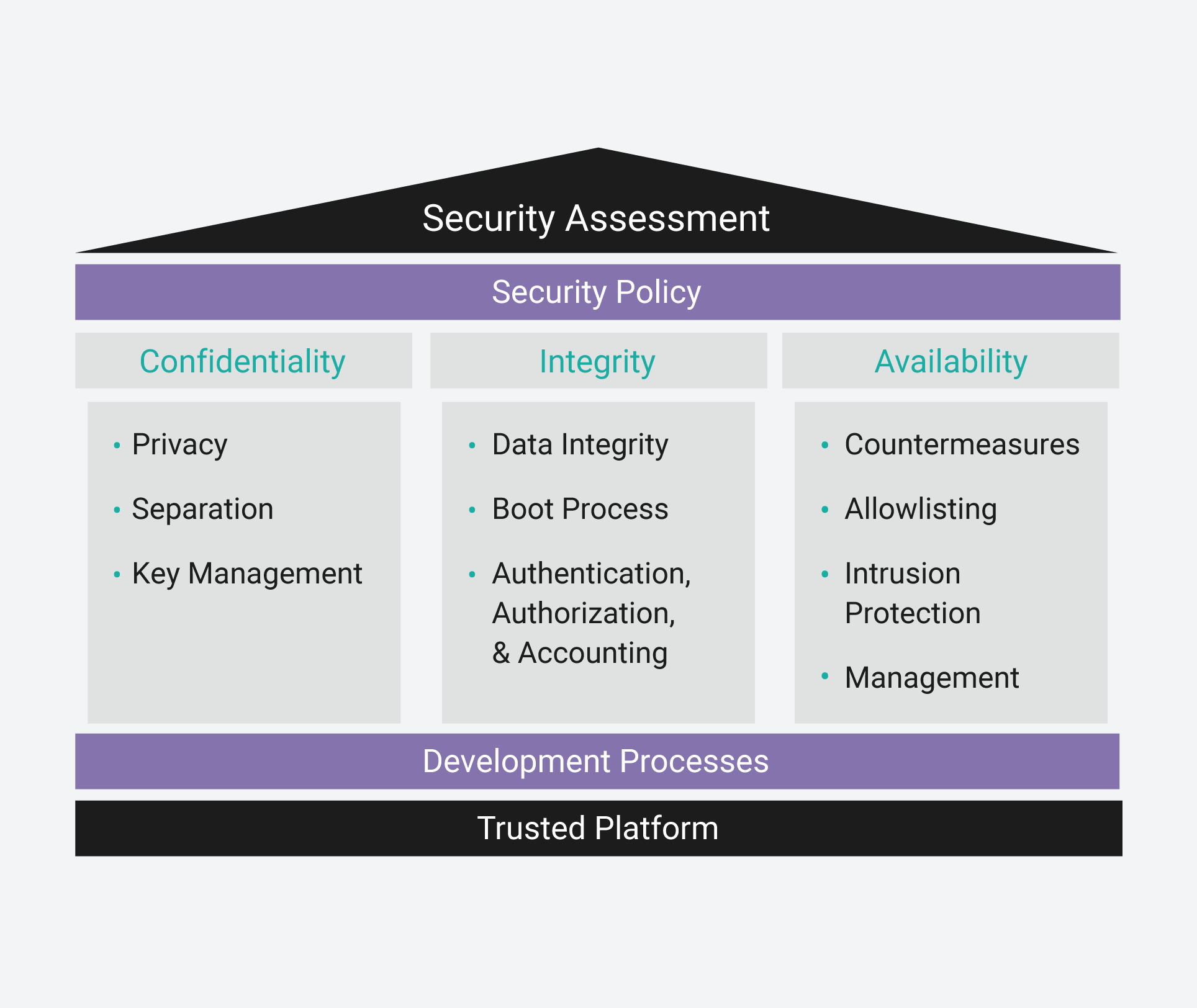
Similar to IT systems, an embedded security policy uses the CIA triad as a model for policy development. The CIA triad defines the principles needed to protect a device from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This model helps development teams think about the different aspects of security for their project. The CIA acronym stands for confidentiality, integrity, and availability.

The CIA triad helps define security needs for embedded systems.
Confidentiality implementations are used to protect the privacy of data in embedded systems. This includes data in motion, data at rest or stored on the device, data being processed by the device, and data passing to and from the device.
Integrity implementations ensure that the embedded device data has not been modified or deleted by an attacker. This includes data being generated or consumed by the embedded device as well as its programming data (the operating system, applications, configurations data, etc.).
Availability implementations ensure that an embedded device performs its intended function. This means an attacker cannot change a device’s intended functional purpose. This is of paramount importance to devices that perform life- or mission-critical tasks.
A security assessment provides a systematic approach to defining protection for the various assets of a project. Wind River ® Professional Services offers security assessments for embedded customers starting a new project; these assessments include a variety of security characteristics:
As embedded systems, IoT devices, and the intelligent edge grow in numbers of deployments and new use cases, so does the attack surface and potential for security breaches. Every connected device, from small IoT home thermostats to the most sophisticated systems of systems, holds one or more potential points of entry that can be exploited by a cyberattack. With billions of devices already connected and tens of billions more coming, securing devices and protecting the data they generate is imperative.
In the embedded industry, there is a high degree of trust that companies are adhering to and implementing the most up-to-date standards for security requirements and functionality. For embedded systems with mission-critical and safety-critical applications, a comprehensive and full lifecycle security architecture is essential. Without a security-first policy, no device can be truly secure and remain secure over its deployed lifetime.
Security for software development The software development infrastructure, where code is developed, tested, and compiled, requires extra security safeguards to ensure that there are no opportunities for either internal or external malicious actors. Many embedded developers use DevOps tools and building blocks from multiple sources. These tools and building blocks should come only from trusted sources and should include a software bill of materials. The components of the development environment should be actively monitored for CVEs and events that violate the system’s security policy. In addition, the development infrastructure should provide strict identity management and access protection to authorized individuals only. Privileged actions within the system should require multiple parties’ approval and performance.

Designing a secure embedded system is a full lifecycle process, starting before the first line of code is written.
Security for Devices — Hardware and Operating System Software The software and hardware used for embedded devices can include built-in security functionality. Some of the most commonly enabled hardware security features include secure boot, attestation, cryptographic processing, random-number generation, secure key storage, physical tamper monitoring, and JTAG protection. To fully leverage the hardware features, operating system software requires device drivers specific to the architecture of the underlying processor. Operating system software can also come with built-in security functionality. The VxWorks ® RTOS includes built-in security features for secure boot (digital signed images), secure ELF loader for digitally signed applications, secure storage for encrypted containers and full disk encryption, kernel hardening, and much more. (See the VxWorks datasheet for a full list.) The Linux operating system also provides a number of security packages developers can use to help secure their OS platform build. Wind River Linux, a commercially provided Yocto Project–based build system, includes more than 250 verified and validated security packages. The Linux operating system can also be hardened to provide anti-tamper and cybersecurity capabilities.
Security for embedded applications and container-based applications Embedded applications are the software designed to perform the function or specific task of an embedded system. Embedded applications run on top of the embedded operating system. Even if the underlying OS is secure, applications can require additional security features, including security testing, the use of code-scanning tools to improve security, and constant monitoring and prompt fixing of security issues. Container-based applications are starting to be used in embedded systems. These applications are constantly processing data, generating log files, and caching files. Application of critical security controls are put in place to ensure that application activities are not malicious.
Security to protect data Embedded systems, IoT devices, and intelligent edge systems all process, store, and transport data. Mission-critical and safety-critical applications rely on the integrity of the data to perform intended functions, so it is essential that the embedded system has the right security functionality to prevent data leakage. This means the data, whether in motion, at rest, or in use, is fully encrypted and protected.
Security services Security is an ongoing effort for embedded systems. It is a full lifecycle activity, from design to decommissioning. For many companies, monitoring and maintaining a device’s security posture for its full life can be best served by leveraging a third-party entity. Managed security services and security as a service are quickly becoming viable options for resource-constrained teams to get the help they need to detect and respond to threats, continuously monitor and analyze deployment operations, and make data-driven decisions to prevent attacks.
Embedded security is designed to protect the components and software of the device. It includes features to protect the hardware, operating system, application, and data. Cybersecurity refers to additional security features that protect a device from network-initiated attacks. Both forms of security are necessary for embedded systems, IoT products, and intelligent edge devices.